Mac Os X Tiger For Intel X86
- Mac Os X 10.4 Tiger Intel X86 Dmg
- Free Mac Os X Tiger Software
- Mac Os X Tiger For Intel X86 Iso
- Mac Os X Tiger Features
It is also the last Mac OS X version that supports PowerPC-based applications, as Mac OS X v10.7 'Lion' dropped support for Rosetta. In 2020, 15 years following the announcement to transition to Intel processors, Apple announced a transition of the Macintosh to ARM -based processors developed in-house. Mac OS X 10.4.10.x86 Source. Why you'll love to develop on your Mac Open Source in macOS. Learn about the 200+ open source projects that ship with macOS. Patr1ck writes 'Mac Daily News is reporting that Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger for x86 processors has been leaked to the internet already. Apparently the version running on the development kit machines is easily transfered to run on any x86 machine. Conspiracy theorists unite: an Apple marketing scheme?'
Voici quelque distribution OSx86 de toute les version de Mac OS X (de 10.4 a 10.9) TORRENT MAGNET LINK. Note les information sont placer comem ceci.
(There's no video for Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger for PPC yet. Please contribute to MR and add a video now!)
Download Mac Os X 10.4 Tiger For Intel X86, Bootable And. 26 Jan 07, Download torrent Mac OS X 10.4.4 Restore Disc.dmg. Mac OS X Tiger Server is a server-focussed release of Tiger with. With compatible Macs using both PowerPC and Intel processors. Serial: xsvr-104-000-r-6d7-rj4-psn-bpy-sfx-2fn-2. QEMU is a Virtual Machine system a bit like VirtualBox or VMware except if VT-X is not supported by your CPU, there is a good chance QEMU can still run OS X! It may be theoretically possible to have a download and boot script that runs OS X on a broad array of x8664 computers. But for now that's another story.
What is Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger for PPC? This is the retail DVD version of Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger for Macs using the PowerPC architecture. (Will not work on Intel Macs). Mac_OS_X_tiger.iso(2701.06 MiB / 2832.27 MB) Mac OS X 10.4 (Tiger) Install CD / ISO image 421 / 2017-12-15 / 2018-01-08 / e733683208d8eb71afe5f10f2ff377ca223f3a35 / 2Z691-5305-A / /
Architecture: PPC only (300Mhz or faster G3, G4, or G5 CPU) Firewire port Kasauti zindagi ki 2 wiki. 256MB of RAM 3GB Hard disk space DVD drive Might work under PearPC Emulating this? It should run fine under: QEMU |
| A version of the macOS operating system | |
| Developer | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| OS family | |
| Source model | Closed, with open source components |
| Released to manufacturing | April 29, 2005; 14 years ago[1] |
| Latest release | 10.4.11 / November 14, 2007; 11 years ago |
| Update method | Apple Software Update |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, PowerPC |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (XNU) |
| License | Commercialproprietary software[2] |
| Preceded by | Mac OS X 10.3 Panther |
| Succeeded by | Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard |
| Official website | Apple - Mac OS X at the Wayback Machine (archived July 28, 2006) |
| Support status | |
| Obsolete, unsupported as of September 2009, Safari support ended November 2010.[3] | |
| Part of a series on |
| macOS |
|---|
Mac OS X Tiger (version 10.4) is the fifth major release of Mac OS X (now named macOS), Apple's desktop and serveroperating system for Mac computers. Tiger was released to the public on April 29, 2005 for US$129.95 as the successor to Mac OS X 10.3 Panther. Some of the new features included a fast searching system called Spotlight, a new version of the Safari web browser, Dashboard, a new 'Unified' theme, and improved support for 64-bit addressing on Power Mac G5s. Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger shocked executives at Microsoft by offering a number of features, such as fast file searching and improved graphics processing, that Microsoft had spent several years struggling to add to Windows with acceptable performance.[4]
- Jun 12, 2005 - If the torrent doesn't show up pretty quickly, and its late already, it doesn't exist. Report: Apple Mac OS X 10.4.1 for Intel hits piracy sites. It lets you easily convert to ISO as well as other imaging formats, and it lets you.
- Patr1ck writes 'Mac Daily News is reporting that Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger for x86 processors has been leaked to the internet already. If the torrent doesn't show up pretty quickly, and its late already, it doesn't exist. I estimate that we're down to a matter of hours before Mac OS X 10.4.1 for Intel hardware is available for download on.
Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger was included with all new Macs, and was also available as an upgrade for existing Mac OS X users, or users of supported pre-Mac OS X systems. The server edition, Mac OS X Server 10.4, was also available for some Macintosh product lines. Six weeks after its official release, Apple had delivered 2 million copies of Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger, representing 16% of all Mac OS X users. Apple claimed that Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger was the most successful Apple OS release in the company's history.[5] At the WWDC on June 11, 2007, Apple's CEO, Steve Jobs, announced that out of the 22 million Mac OS X users, more than 67% were using Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger.[6]
Apple announced a transition to Intel x86 processors during Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger's lifetime, making it the first Apple operating system to work on Apple–Intel architecture machines. The original Apple TV, released in March 2007, shipped with a customized version of Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger branded 'Apple TV OS' that replaced the usual GUI with an updated version of Front Row.[7]
Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger was succeeded by Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard on October 26, 2007, after 30 months, making Mac OS 10.4 Tiger the longest running version of Mac OS X.[8] The last security update released for Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger users was the 2009-005 update.[9][10] The next security update, 2009-006[11] only included support for Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard and Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard. The latest supported version of QuickTime is 7.6.4. The latest version of iTunes that can run on Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger is 9.2.1, because 10.0 only supports Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard and later.[12] Safari 4.1.3 is the final version for Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger as of November 18, 2010.[13] Despite not having received security updates since then, Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger remains popular with Power Mac users and retrocomputing enthusiasts due to its wide software and hardware compatibility, as it is the last Mac OS X version to support the Classic Environment, a Mac OS 9 compatibility layer, and PowerPC G3 processors.[14]
- 3New and changed features
- 4Improvements
System requirements[edit]
Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger was initially available in a PowerPC edition, with an Intel edition released beginning at Mac OS X 10.4.4 Tiger. There is no universal version of the client operating system, although Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger Server was made available on a universal DVD from version Mac OS X 10.4.7 Tiger. While Apple shipped the PowerPC edition bundled with PowerPC-based Macs and also sold it as a separate retail box, the only way to obtain the Intel version was to buy an Intel-based Mac bundled with it. However, it was possible to buy the 'restore' DVDs containing the Intel version through unofficial channels such as eBay, and officially through Apple if you could provide proof of purchase of the appropriate Intel Mac. These grey-colored ‘restore’ DVDs supplied with new Macs, are designed to only restore on the model of Mac that they are intended for. However, they can be modified to work on any Intel Mac. The retail PowerPC-only DVD can be used on any PowerPC-based Mac supported by Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger.
The system requirements of the PowerPC edition are:[15]
- A PowerPC G3, G4, or G5 processor running at 300 MHz or faster
- Built-in FireWire
- At least 256 megabytes (MB) of RAM, 512 MB recommended (128 MB can run it unofficially)
- At least 3 GB of available hard disk space; 4 GB of disk space including the Xcode 2 Tools, 2 GB for the minimal install
- DVD-ROM drive (CD-ROM exchange was available; offer ended on March 20, 2007)
Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger removed support for older New World ROM Macs such as the original iMacs and iBooks that were supported in Mac OS X 10.3 Panther; however it is possible to install Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger on these Macs using third-party software (such as XPostFacto) that overrides the checks made at the beginning of the installation process. Likewise, machines such as beige Power Mac G3s and ‘Wall Street’ PowerBook G3s that were dropped by Mac OS X 10.3 Panther can also be made to run both Mac OS X 10.3 Panther and Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger in this way. Also, Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger can be installed on unsupported New World ROM Macs by installing it on a supported Mac, then swapping hard drives. Old World ROM Macs require the use of XPostFacto to install Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger.
Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger was the last version of Mac OS X to support the PowerPC G3 processor.
History[edit]
Apple CEO Steve Jobs first presented Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger in his keynote presentation at the WWDC on June 28, 2004, ten months before its commercial release in April 2005. Four months before that official release, several non-commercial, developer's releases of Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger leaked onto the internet via BitTorrent file sharers. It was first mentioned on Apple's website on May 4, 2004. Apple sued these file sharers.[16] On April 12, 2005, Apple announced Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger's official, worldwide release would be April 29. All Apple Stores around the world held Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger seminars, presentations and demos.
On June 6, 2005 at the WWDC in San Francisco, Jobs reported that nearly two million copies had been sold in Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger's first six weeks of release, making Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger the most successful operating system release in Apple's history. Jobs then disclosed that Mac OS X had been engineered from its inception to work with Intel's x86 line of processors in addition to the PowerPC, the CPU for which the operating system had always been publicly marketed. Apple concurrently announced its intent to release the first x86-based computers in June 2006, and to move the rest of its computers to x86 microprocessors by June 2007. On January 10, 2006, Apple presented its new iMac and MacBook Pro computers running on Intel Core Duo processors, and announced that the entire Apple product line would run on Intel processors by the end of 2006. Apple then released the Mac Pro and announced the new Xserve on August 8, completing the Intel transition in 210 days, roughly ten months ahead of the original schedule.
Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger is the first version of Mac OS X to be supplied on a DVD, although the DVD could originally be exchanged for CDs for $9.95. It is also the first (and so far only) version of Mac OS X that would eventually have an update version number ending with a value greater than 9, as the last version of Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger was 10.4.11.
New and changed features[edit]
End-user features[edit]
Apple advertises that Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger has over 150 new and improved features, including:
- Spotlight — Spotlight is a full-text and metadata search engine, which can search everything on one's Mac including Microsoft Word documents, iCal calendars and Address Book contact cards. The feature is also used to build the concept of ‘smart folders’ into the Finder. Spotlight will index files as they are saved, so they can be quickly and easily found through a search-as-you-type box in the menu bar. As a side-effect, it adds hidden folders and indexing files to removable media like USB flash drives.
- iChat AV — The new iChat AV 3.0 in Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger supports up to four participants in a video conference and ten participants in an audio conference. It also now supports communication using the XMPP protocol. A XMPP server called iChat Server is included on Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger Server.
- Safari RSS — The new Safari 2.0 web browser in Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger features a built-in reader for RSS and Atomweb syndication that can be accessed easily from an RSS button in the address bar of the web browser window. An updated version of Safari, included as part of the free Mac OS X (10.4.3 Tiger update, can also pass the Acid2 web standards test.
- Mail 2 — The new version of Mail.app email client included in Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger featured an updated interface, 'Smart Mailboxes', which utilizes the Spotlight search system, parental controls, as well as several other features.
- Dashboard — The Dashboard is a new mini-applications layer based on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which returns the desk accessories concept to the Mac OS. These accessories are known as widgets. It comes with several widgets such as Weather, World Clock, Unit Converter, and Dictionary/Thesaurus. More are available for free online. Its similarity to the Konfabulator application caused some criticism.[17]
- Automator — A scripting tool to link applications together to form complex automated workflows (written in AppleScript, Cocoa, or both). Automator comes with a complete library of actions for several applications that can be used together to make a Workflow.
- VoiceOver — screen reader interface similar to Jaws for Windows and other Windows screen readers that offers the blind and visually impaired user keyboard control and spoken English descriptions of what is happening on screen. VoiceOver enables users with visual impairment to use applications via keyboard commands. VoiceOver is capable of reading aloud the contents of files including web pages, mail messages and word processing files. Complete keyboard navigation lets the user control the computer with the keyboard rather than the mouse, a menu is displayed in a window showing all the available keyboard commands that can be used.
- A complete built-in Dictionary/Thesaurus based on the New Oxford American Dictionary, Second Edition, accessible through an application, Dictionary, a Dashboard widget, and as a system-wide command (see below).
- .Mac syncing — Though this is not a new feature, .Mac syncing in Tiger is much improved over Panther. Syncing tasks in Tiger are now accomplished through the .Mac system preferences pane rather than the iSync application.
- QuickTime 7 — A new version of Apple's multimedia software has support for the new H.264/AVC codec, which offers better quality and scalability than other video codecs.[citation needed] This new codec is used by iChat AV for clearer video conferencing. New classes within Cocoa provide full access to QuickTime for Cocoa application developers. The new QuickTime 7 player application bundled with Tiger now includes more advanced audio and video controls as well as a more detailed Information dialog, and the new player has been rebuilt using Apple's Cocoa API to take advantage of the new technologies more easily.
- New Unix features — New versions of cp, mv, and rsync that support files with resource forks. Command-line support for features like the above-mentioned Spotlight are also included.
- Xcode 2.0 — Xcode 2.0, Apple's Cocoa development tool now includes visual modelling, an integrated Apple Reference Library and graphical remote debugging.
New applications in Tiger[edit]
- Automator — Automator uses workflows to process repetitive tasks automatically
- Grapher — Grapher is a new application capable of creating 2D and 3D graphs similar to those of Graphing Calculator.
- Dictionary — A dictionary and thesaurus program that uses the New Oxford American Dictionary. It has a fast GUI for displaying the Dictionary, and allows the user to search the dictionary with Spotlight, to print definitions, and to copy and paste text into documents. Dictionary also provides a Dictionary service in the Application menu, and Cocoa and WebKit provides a global keyboard shortcut (ctrl-⌘-D by default) for all applications that display text with them. Its use was furthered in the next version of OS X by providing definitions from Wikipedia. The Dictionary application is a more feature-filled version of the Dictionary widget.
- Quartz Composer — Quartz Composer is a development tool for processing and rendering graphical data.
- AU Lab — AU Lab is a developer application for testing and mixing Audio Units.
- Dashboard — Dashboard is a widget application. Tiger widgets include: a calculator, dictionary, a world clock, a calendar, and more (full list). Users can also download and install more widgets.
Improvements[edit]
- An upgraded kernel with optimized kernel resource locking and access control lists, and with support for 64-bituserlandaddress spaces on machines with 64-bit processors.[18]
- An updated libSystem with both 32-bit and 64-bit versions; combined with the aforementioned kernel change, this allows individual applications to address more than 4 GB of memory when run on 64-bit processors, although an application using Apple libraries or frameworks other than libSystem would need to have two processes, one running the 64-bit code and one running the code that requires other libraries and frameworks.[18][19]
- A new startup daemon called launchd that allows for faster booting.
- The printing dialog in Tiger now features a drop down menu for creating PDFs, sending PDFs to Mail, and other PDF related actions. However, the user interface has been criticized for creating a hybrid widget that looks like a plain button but acts like a pop-up menu. This is one of only three places in the entire Mac OS X interface where such an element appears.[citation needed]
- Dock menus now have menu items to open an application at login, or to remove the icon from the dock.
- The Window menu in the Finder now features a 'Cycle Through Windows' menu item.
- The Get Info window for items in the Finder now includes a 'More Info' section that includes Spotlight information tags such as Image Height & Width, when the file was last opened, and where the file originated.
- Early development of resolution independence. Apple notes that this will be a user-level feature in a future version of Mac OS X.[20] Among the changes, the maximum size of icons has been increased to 256x256. However, the Finder does not yet support this size.
Technologies[edit]
- A new graphics processing API, Core Image, leveraging the power of the available accelerated graphics cards.
- Core Image allows programmers to easily leverage programmable GPUs for fast image processing for special effects and image correction tools. Some of the included Image Units are Blur, Color Blending, Generator Filters, Distortion Filters, Geometry Filters, Halftone features and much more.
Mac Os X 10.4 Tiger Torrent
- A new data persistence API, Core Data, that makes it easier for developers to handle structured data in their applications.
- The Mac OS X Core Data API helps developers create data structures for their applications. Core Data provides undo, redo and save functions for developers without them having to write any code.
- A new video graphics API, Core Video, which leverages Core Image to provide real-time video processing.
- Apple's Motion real-time video effects program takes advantage of Core Video in Tiger. Core Video lets developers easily integrate real-time video effects and processing into their applications.
- Core Audio integrates a range of audio functionality directly into the operating system.
Interface differences[edit]
In every major new revision of Mac OS X, Apple alters the graphical user interface somewhat. In Tiger, the menu bar displayed at the top of the screen now features a colored Spotlight button in the upper right corner; the menu itself has a smoother 'glassy' texture to replace the faint pinstripes in Panther.
Also of note, Tiger introduces a new window theme, often described as 'Unified'. A variation on the standard, non-brushed metal theme used since the introduction of Mac OS X, this theme integrates the title bar and the toolbar of a window. A prominent example of an application that utilizes this theme is Mail.
Mac Os X 10.4 Tiger Intel X86 Dmg
Accessibility[edit]
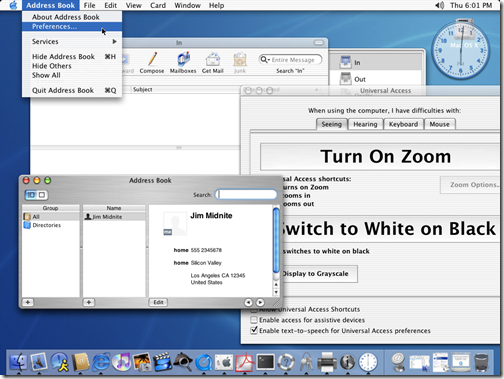
Tiger was the first version of Mac OS X to include the 'Zoom' screen magnifier functionality, which allowed the user to zoom on to the area around the mouse by holding CONTROL and scrolling the mouse wheel up or down (to zoom in and out respectively).[21]
Tiger trademark lawsuit[edit]
Shortly before the release of Mac OS X Tiger, the computer retailer TigerDirect.com, Inc. filed a lawsuit against Apple, alleging that Apple infringed TigerDirect.com's trademark with the Mac OS X Tiger operating system.[22]
The following is a quotation from TigerDirect.com's court memorandum:
- Apple Computer's use of its infringing family of Tiger marks to expand sales of products besides its operating system software is already evident — for example, Apple Computer is offering free iPods and laptops as part of its Tiger World Premiere giveaway. In short, notwithstanding its representation to the PTO that it would only use Tiger in connection with their unique computer operating system software, Apple Computer has in recent weeks used a family of Tiger marks in connection with a substantially broader group of products and services, including the very products and services currently offered by Tiger Direct under its famous family of Tiger marks.[23]
English sinhala dictionary online. In 2005 TigerDirect was denied a preliminary injunction that would have prevented Apple from using the mark while the case was decided.[24] Apple and TigerDirect reached a settlement in 2006, after which TigerDirect withdrew its opposition.[25]
Support for Intel processors[edit]
| Apple's transition to Intel processors |
|---|
At the 2005 WWDC, Apple CEO Steve Jobs announced that Apple would begin selling Mac computers with Intel processors in 2006. To allow developers to begin producing software for these Intel-based Macs, Apple made Developer Transition Kits available for sale that included a version of Mac OS X v10.4.1 designed to run on x86 processors.
This build includes Apple's Rosetta — a translation process that allows Intel processor versions of the OS to run PPC software with little penalty. This is contrasted with the contemporary Mac OS 9 Classic mode, which uses comparably larger amounts of system resources.
Soon after the Developer Transition Kits began shipping, copies of Tiger x86 were leaked onto file sharing networks. Although Apple had implemented a Trusted ComputingDRM scheme in the transition hardware and OS in an attempt to stop people installing Tiger x86 on non-Apple PCs, the OSx86 project soon managed to remove this restriction.[26] As Apple released each update with newer safeguards to prevent its use on non-Apple hardware, unofficially modified versions were released that circumvented Apple's safeguards. However, with the release of 10.4.5, 10.4.6, and 10.4.7 the unofficially modified versions continued to use the kernel from the 10.4.4 because later kernels have hardware locks and depend heavily on EFI. By late 2006, the 10.4.8 kernel had been cracked.[27]
At MacWorld San Francisco 2006, Jobs announced the immediate availability of Mac OS X v10.4.4, the first publicly available release of Tiger compiled for both PowerPC and Intel x86-based machines.
Free Mac Os X Tiger Software
Release history[edit]
| Version | Build | Date | OS name | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.4 | 8A428 | April 29, 2005 | Darwin 8.0 | Preinstalled on much of new line |
| 8A432 | Original retail release | |||
| 10.4.1 | 8B15 | May 16, 2005 | Darwin 8.1 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.1 Update |
| 8B17 | May 19, 2005 | Server edition | ||
| 10.4.2 | 8C46 | July 12, 2005 | Darwin 8.2 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.2 Update (Delta) |
| 8C47 | Server edition | |||
| 8E102 | October 12, 2005 | Exclusively for Front RowiMac G5 released on same date | ||
| 8E45 | October 19, 2005 | Exclusively for PowerBook G4s released on same date | ||
| 8E90 | Exclusively for Power Mac G5 Dual and Quad released on same date | |||
| 10.4.3 | 8F46 | October 31, 2005 | Darwin 8.3 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.3 Update (Delta) Updated retail release |
| 10.4.4 | 8G32 | January 10, 2006 | Darwin 8.4 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.4 Update (Delta) PowerPC |
| 8G1165 | Shipped on initial Intel-based Macs | |||
| 10.4.5 | 8H14 | February 14, 2006 | Darwin 8.5 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.5 Update (delta) PowerPC |
| 8G1454 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.5 Update (delta) Intel | |||
| 10.4.6 | 8I127 | April 3, 2006 | Darwin 8.6 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.6 Update (delta) PowerPC; Final retail release |
| 8I1119 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.6 Update (delta) Intel | |||
| 10.4.7 | 8J135 | June 27, 2006 | Darwin 8.7 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.7 Update (delta) PowerPC |
| 8J2135a | About the Mac OS X 10.4.7 Update (delta) Intel | |||
| 8K1079 | August 7, 2006 | exclusively for Mac Pro released the same date | ||
| 8N5107 | exclusively for Apple TV (formerly codenamed iTV)[28] | |||
| 10.4.8 | 8L127 | September 29, 2006 | Darwin 8.8 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.8 Update (delta)] PowerPC |
| 8L2127 | Update (delta) Intel and Universal Server Edition | |||
| 10.4.9 | 8P135 | March 13, 2007 | Darwin 8.9 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.9 Update (delta) PowerPC |
| 8P2137 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.9 Update (delta) Intel and Universal Server Edition | |||
| 10.4.10 | 8R218 | June 20, 2007 | Darwin 8.10 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.10 Update (delta) PowerPC |
| 8R2218 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.10 Update (delta) Intel and Universal Server Edition | |||
| 8R2232 | ||||
| 10.4.11 | 8S165 | November 14, 2007 | Darwin 8.11 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.11 Update PowerPC |
| 8S2167 | About the Mac OS X 10.4.11 Update Intel and Universal Server Edition |
References[edit]
- ^'Apple Unleashes 'Tiger' Friday at 6:00 p.m.' (Press release). Apple Inc. April 28, 2005.
- ^'SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR MAC OS X Single Use License'(PDF). apple.com. Apple Inc. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
- ^Gregg Keizer (December 17, 2013). 'Apple signals end to OS X Snow Leopard support'. Computerworld.
The company did the same for OS X Tiger, officially known as OS X 10.4, which was retired from support in September 2009, more than four years after its introduction.
- ^Gregg Keizer (January 29, 2007). 'Microsoft's Vista Had Major Mac Envy, Company E-Mails Reveal'. Information Week. Retrieved August 9, 2017.
- ^Peter Cohen and Jason Snell (June 6, 2005). 'WWDC 2005 Keynote Live Update'. Macworld.com. Retrieved July 10, 2006.
- ^Apple Inc. (June 11, 2007). 'WWDC 2007 Keynote'.
- ^'Apple TV OS successfully booted on Macs'. MacNN. March 27, 2007. Retrieved April 15, 2007.
- ^Knight, Dan (April 13, 2007). 'Leopard Delayed to October. And the Bad Thing Is?'. LowEnd Mac. Cobweb Publishing, Inc. Retrieved December 9, 2007.
- ^Apple Inc. (September 10, 2009). 'Security Update 2009-005 (Tiger PPC)'.
- ^Apple Inc. (September 10, 2009). 'Security Update 2009-005 (Tiger Intel)'.
- ^Apple Inc. (November 9, 2009). 'About Security Update 2009-006 / Mac OS X v10.6.2'. Archived from the original on November 13, 2009.
- ^Apple Inc. (September 1, 2010). 'iTunes 10'. Archived from the original on September 5, 2010.
- ^Apple Inc. (November 18, 2010). 'Apple security updates'. Retrieved November 18, 2010.
- ^Low End Mac (April 29, 2011). '6 Years With Tiger'.
- ^Apple. 'Mac OS X Tiger: System requirements'. Apple. Retrieved October 18, 2009.
- ^'Apple sues 'Tiger' file sharers'. BBC News. London: BBC. December 22, 2004. Retrieved December 9, 2007.
- ^John Siracusa (April 28, 2005). 'Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger'. p. 17. Retrieved June 11, 2006.
- ^ abJohn Siracusa (April 28, 2005). 'Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger'. ArsTechnica.com. p. 4. Retrieved February 25, 2007.
- ^Apple (March 6, 2006). 'Developing 64-bit applications'. Apple Developer Connection. Retrieved March 5, 2007.
- ^'Resolution Independent UI'. Apple Developer Connection. Retrieved July 10, 2006.
- ^'Universal Access'. Apple Inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2005.
- ^AppleInsider Staff (April 28, 2005). 'Apple sued over 'Tiger,' injunction sought'. AppleInsider. Retrieved July 10, 2006.
- ^lawyerguy (April 28, 2005). 'Some points for TigerDirect'. Slashdot. Retrieved July 10, 2006.
- ^Kasper Jade (May 13, 2005). 'Court sides with Apple over 'Tiger' trademark dispute'. AppleInsider. Retrieved August 10, 2006.
- ^'Trademark Trial and Appeal Board, proceeding 91163437'. May 8, 2006.
- ^Mark Baard (August 12, 2005). 'Mac Hacks Allow OS X on PCs'. Wired News. Retrieved July 10, 2006.
- ^Tony Smith (October 25, 2006). 'Mac OS X 10.4.8 runs on any PC..' Reg Hardware (The Register). Retrieved December 16, 2006.
- ^'Apple TV OS 10.4.7 - AwkwardTV'. Wiki.awkwardtv.org. Archived from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
External links[edit]
Mac Os X 10.4 Tiger Download
- Archive copy of official website at the Wayback Machine (archived June 9, 2011)
- Ars Technica Mac OS X Tiger Review at Ars Technica
- Mac OS X Tiger at Wikibooks
| Preceded by Mac OS X 10.3 | Mac OS X 10.4 2005 | Succeeded by Mac OS X 10.5 |
Comments are closed.
macOS (formerly Mac OS X) is an operating system for Apple Macintosh computers,[1] first released to the public on March 24, 2001, developed by Apple. It is the successor to Mac OS 9, hence the X signifying both its Unix roots and the major release version number 10. As mentioned by Apple, Wikipedia, and others, it is said as Mac OS 10. It shares none of the 'Classic' Mac OS design, and is completely rewritten and uses Next frameworks, a hybrid XNU/Mach kernel, and a BSD subsystem dubbed 'Darwin'. While underlying components of OS X are free/open source software, the top layers, such as the Aqua UI, are proprietary; Darwin packages can be downloaded and compiled from the Apple Open Source website to make a bootable OS.
Mac OS X has been built for three different architectures and four platforms during its release cycle to date. The first six releases (10.0.0-10.5.8) were designed for the PowerPC architecture, adding 64-bit PowerPC support as an additional platform for the G5 in 10.3 Panther. Intel (x86) support started with 10.4.4 Tiger, and was built as a universal release for both PowerPC/x86 with 10.5 Leopard, which finally dropped all G3 support. Since 10.6, PowerPC support is non-existent/dropped, and Mac OS X is currently designed for Mac computers with Intel 32-bit (x86) and Intel 64-bit (x86_64) architectures. AMD is not currently officially supported. Starting with 10.7 'Lion', Mac OS X is now referred to simply as 'OS X'.[2]
The 'iPhone OS' or iOS, which powers the iPhone, iPod touch, and iPad[3] is a direct descendant of OS X, and shares its design and many internal frameworks. The previous version of OS X is 'Yosemite' (10.10), released on October 16, 2014.[4] macOS Sierra (10.12 internally) is currently in development, scheduled for this Fall.[5] Developer previews and Public Betas are available.[6]
- 1Versions
- 1.1Classic
Versions
Classic
BYTE Build
Screenshots of this build were provided in the BYTE magazine in 1984. This version has a black default background and has the Arrange menu.
System 0.85
- See System 0.85
System 0.97
- See System 0.97
System 1.1d
An update to 0.97, had slight changes but is otherwise the same. The most common version of pre-System 6 OS'es.
System 1.1g
System 1.1g kernel with 2 disks packed with developing / debugging software. This used to be a rare version of the Mac OS until it was released on BetaArchive.
System 1.1h
Not much is known about this odd version, but we do know that it exists.
System 2.x
Technically the same as System 1.1, yet has several bug fixes. Recommended for your 128k if you can't get ahold of System 3.x.
System 6
System 6 was a version of Mac OS, It was released on April 1988. The operating system of the Apple Macintosh computer, which was used in the late 1980s prior to the introduction of System 7. It is still widely considered to be the best system software version for the Macintoshes compatible with it. Cooperative multitasking made its Macintosh debut in March 1985 with a program called Switcher, which allowed the user to launch multiple applications and switch between them. However, many programs and features did not function correctly with Switcher, and it did not come with the operating system, so it had to be acquired from Apple separately. System 6 featured a much more seamless approach called MultiFinder. MultiFinder originally debuted with System 5 (System file 4.2 / Finder 6.0). Multitasking under System 6 was optional — startup could be set to Finder or MultiFinder. If MultiFinder was selected, the Finder and its functions continued to run when an application was launched. The MultiFinder environment allowed users to see past the windows of running applications to view Finder icons such as the Trash, or the windows of other applications running in the background.
Mac OS 7
System 7 (codenamed Big Bang) was initially released in May 1991.
Versions 7.0 to 7.1.1 only worked on the 68k platform; 7.1.2 added support for PowerPC processors.
Mac OS 8
Released on July 26, 1997. It had the codename 'Tempo'.
Initially, the early beta releases of the product which were circulated to developers and Apple internal audiences, were branded as Mac OS 7.7 (superseding the current release, Mac OS 7.6). Afterwards, the software was later renamed to Mac OS 8 before the final release.
The fist two releases of Mac OS 8 still could be run on Motorola 68k processors, however version 8.5 dropped support for the 68k platform, only supporting PowerPC based Macintoshes.
Mac OS 9
Released on October 23, 1999, codenamed 'Sonata'.
Apple discontinued development of Mac OS 9 in May 2002.
Mac OS X: 2001-2015
| Release | Version | Internal name | Architecture | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mac OS X Server 1.x | 1.0-1.2.3 | Rhapsody 5.3 | G3 Beige - early G4 (ppc) | Early developer releases of Mac OS X based on the Rhapsody OS. |
| Mac OS X Public Beta | 10.0.1H39 | Kodiak | G3 Beige - G4 (ppc32) | Official beta for participating users; famously had no Apple menu. |
| Mac OS X Cheetah | 10.0 | Cheetah | G3 Beige - G4 (ppc32) | The gold release of Mac OS X. While revolutionary, Cheetah was slow and lacked labels, burn support, and other features. |
| Mac OS X Puma | 10.1 | Puma | G3 Beige - G4 (ppc32) | Incremental update to 10.0, which fixed bugs, optimized the system, and added Burn support. Offered free to affected 10.0 users at the time. |
| Mac OS X Jaguar | 10.2 | Jaguar | G3 Beige - G4 (ppc32) | First major upgrade for Mac OS X, with a marketed 150 new features. It is also the first to sport a feline theme and its codename on the box. |
| Mac OS X Panther | 10.3 | Panther | G3/G4 (ppc32), G5 (ppc64) | Second major upgrade for Mac OS X. Introduced Expose, FileVault, rapid search APIs, G5 support, and a new Finder. |
| Mac OS X Tiger | 10.4 | Tiger | G3/G4 (ppc32), G5 (ppc64), x86/x64 | Introduced Spotlight, Dashboard, H.264 support, and was the first to run on x86 (10.4.7+). It is the longest running release ever with 11 updates. |
| Mac OS X Leopard | 10.5 | Leopard | G4 (ppc32), G5 (ppc64), x86/x64 | Introduced Cocoa Finder with QuickLook, Spaces, Time Machine, and visual overhaul. Last version to support G4/G5, and only unified x86/x64/ppc(64) release on one disc. |
| Mac OS X Snow Leopard | 10.6 | Snow Leopard | Intel x86/x64 | Optimized $29 successor to 10.5. It is the last version for 32-bit x86 (Core Solo/Duo). |
| Mac OS X Lion | 10.7 | Lion | Intel x64 | First release to require x64, and the first digital (non-optical) release. Introduced Autosave, fullscreen app support, Mission Control, the Mac App Store, Launchpad, and many other features for $19.99. It is the last release to not require efi64 (late 2008 and later). |
| OS X Mountain Lion | 10.8 | Mountain Lion | Intel x64 | $19.99 upgrade to Lion, with Gatekeeper, better memory protection, improved scrolling and Autosave control, tweaked applications, and new iOS inspired applications (Notes, Reminders). Dropped 'Mac' in the OS X title, and requires an x64 EFI, which obsoleted several 64-bit Macs. |
| OS X Mavericks | 10.9 | Mavericks | Intel x64 | First release to drop the feline theme, named after California landmarks. First release of OS X since 10.1 to be free to Mac users. Introduced major core system improvements since Snow Leopard, including timed coalescing, memory compression, and energy tweaks. |
| OS X Yosemite | 10.10 | Yosemite | Intel x64 | Features a redesign of the UI to match iOS 7, Swift, an all-new Spotlight, Handoff support, Continuity, widgets, and more. Adds Extensions (ode to classic), and a dark mode for the Dock and Menubar. |
| OS X El Capitan | 10.11 | El Capitan | Intel x64 | Introduces filters for Spotlight, SIP, and overall improvements to the system like 10.6 and 10.9. |
macOS: 2016-present
| Release | Version | Internal name | Architecture | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| macOS Sierra | 10.12 | Sierra | Intel x64 | Visually changes the name for the first time since 2001. It has added Siri to the Mac, Optimized Storage, watchOS paired unlocking, improved Swift, universal Clipboard and Tabs, and APFS support. It is the first release since 10.8 to shift requirements. |
| macOS High Sierra | 10.13 | High Sierra | ||
| macOS Mojave | 10.14 | Mojave | Ends support for OpenGL and OpenCL in favour of Apple's proprietary Metal graphics API. | |
| macOS Catalina | 10.15 | Catalina | Replaces iTunes with three new apps: Apple Music, Apple Podcasts, and Apple TV. Ends all support for 32-bit applications. | |
| macOS Big Sur | 11.0 | Big Sur |
Timeline
Emulation
There are a few good 68k Macintosh emulators available today, which have been ported to various platforms and operating systems. Most of these emulators can run the full range of 68k Macintosh System Software
There is one PowerPC emulator, SheepShaver, which runs Mac OS System 7.1.2 through 9.0.4, and has been ported to various operating systems. The reason Mac OS 9.1 and up don't run in SheepShaver is that SheepShaver lacks a Memory Management Unit emulator, something that the last few Mac OS Releases needed.
References
Mac Os X Tiger For Intel X86 Iso
- ↑OS X running on Macs OS X page on apple.com
- ↑Mac OS X is now called OS X OS X page on apple.com
- ↑iPhone, iPod Touch and iPad are powered by iOS iOS page on apple.com
- ↑The latest version is 10.11.5 OS X page on apple.com
- ↑Development of macOS Sierra macOS Sierra preview page on apple.com
- ↑Developer Previews Public Betas are available Apple Beta Software Program on apple.comDeveloper preview on developer website of Apple